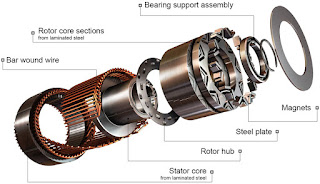
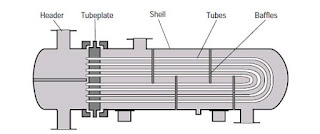
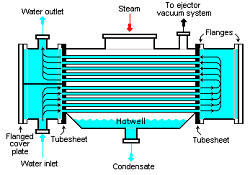
Differences Between forwarding and Survey Reverse Biasing and Linear Potentiometer

The measuring instrument called a potentiometer is essentially a voltage divider used for measuring electric potential (voltage); the component is an implementation of the same principle, hence its name. To answer the question of what is linear potentiometer, first, let us see what are the different parts of this potentiometer. A linear taper potentiometer is usually made up of three pins that adjust to a flow of voltage, and produce a regulated voltage output relevant to its sliding components. Parallel circuits are similar to the smaller blood veins that branch off from an artery and then join in a vessel to return blood to the heart. Now imagine two wires, each as an artery and a vein, that are connected to each other with some smaller wires. These smaller wires have the same voltages applied to them, but different amounts of current flow through them based on the individual wires’ resistance. A circuit composed solely of components connected in series is known as a series circuit;